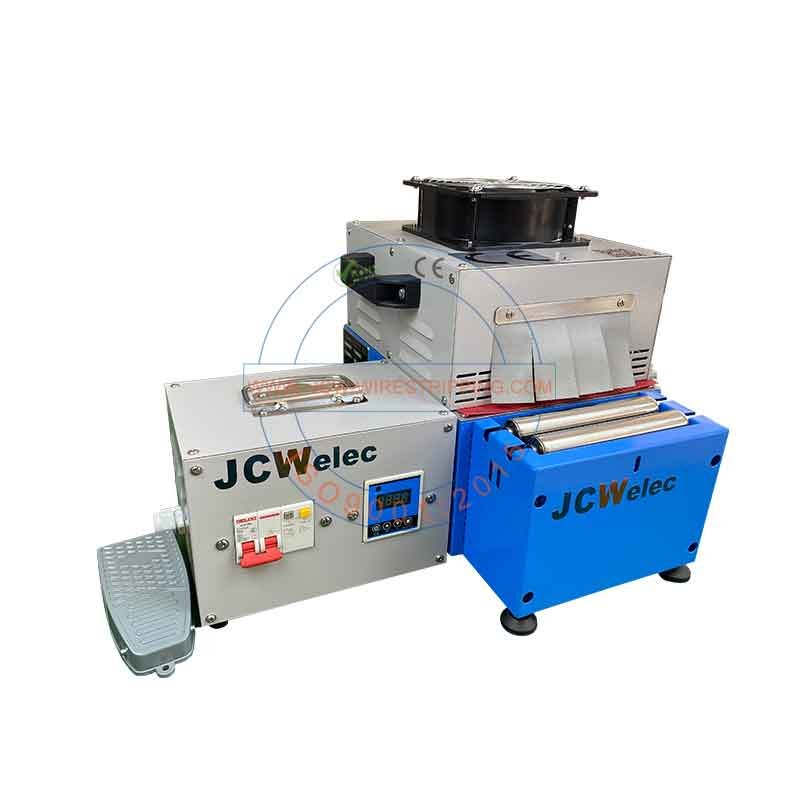
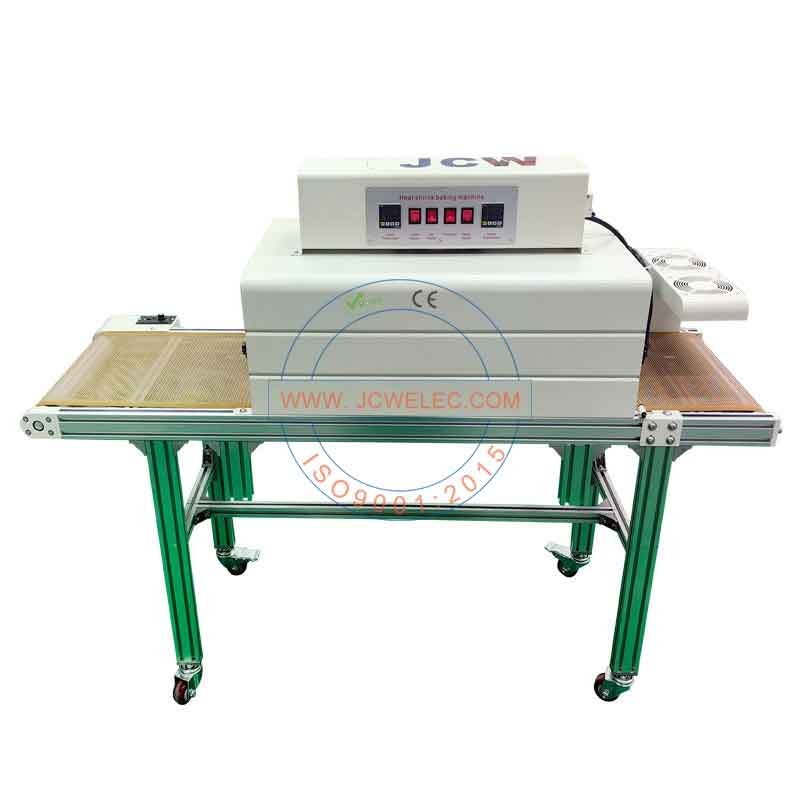
How infrared heating works: Infrared heating is the most basic form of heating. Infrared heaters project heat directly onto the object being heated, without requiring a heat transfer medium or changing the temperature of the space. In addition to rapidly raising the temperature of an object or material, infrared heaters also utilize minimal energy and achieve the desired effect at a low cost.
Advantages of infrared heating: It is environmentally friendly and produces no gaseous products, toxic fumes, or fine particles that could negatively impact the environment.
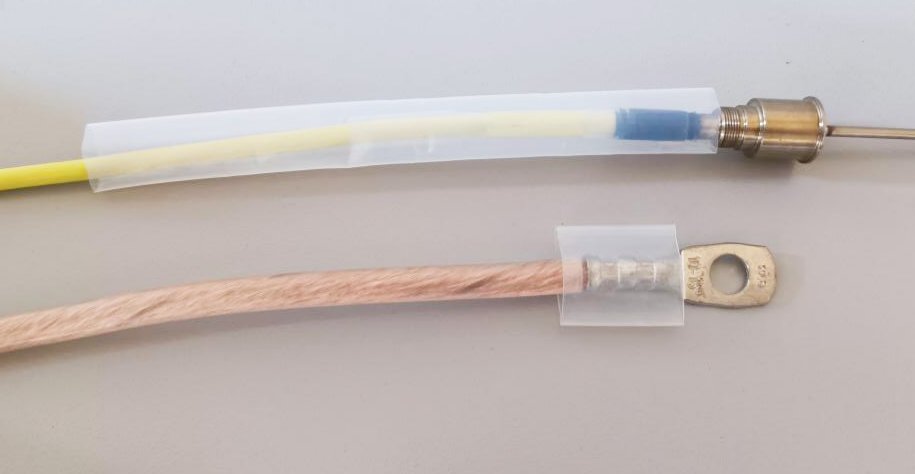
Heat Shrink Tubing Color Requirements: Suitable for dark-colored heat shrink tubing
1. Dark-colored objects absorb infrared rays more strongly, heating up faster under the same conditions and requiring less heating time.
2. Dark-colored objects absorb more infrared energy, converting it into heat.
3. Light-colored objects absorb infrared rays less strongly, heating up more slowly, and may require longer heating times to reach the same temperature.
Why do infrared heating systems for heat-shrink tubing require no temperature control, only time control?
1. Infrared heaters generate short-wavelength infrared radiation to provide extreme heat, making them ideal for high-temperature applications.
2. These infrared heaters use infrared heat to shrink the tubing. Infrared radiation is highly penetrating and requires no heat transfer medium. The heated object directly absorbs the infrared radiation, achieving rapid and even heating. No hot air is required for heating, and the system operates quietly.
3. Infrared radiation reacts quickly, heating as soon as it is turned on. It can quickly raise the temperature of an object, typically completing a heating cycle in 15 to 40 seconds (the duration is adjustable depending on the product). Therefore, these infrared heaters do not require temperature control; only time control is required. Temperature control methods, on the other hand, require a temperature control chip to automatically adjust power and achieve temperature equilibrium. This process also takes 30 to 60 seconds (typically >180 seconds). Only after temperature equilibrium is reached can heating begin.
Equipment Disadvantages and Incompatible Products
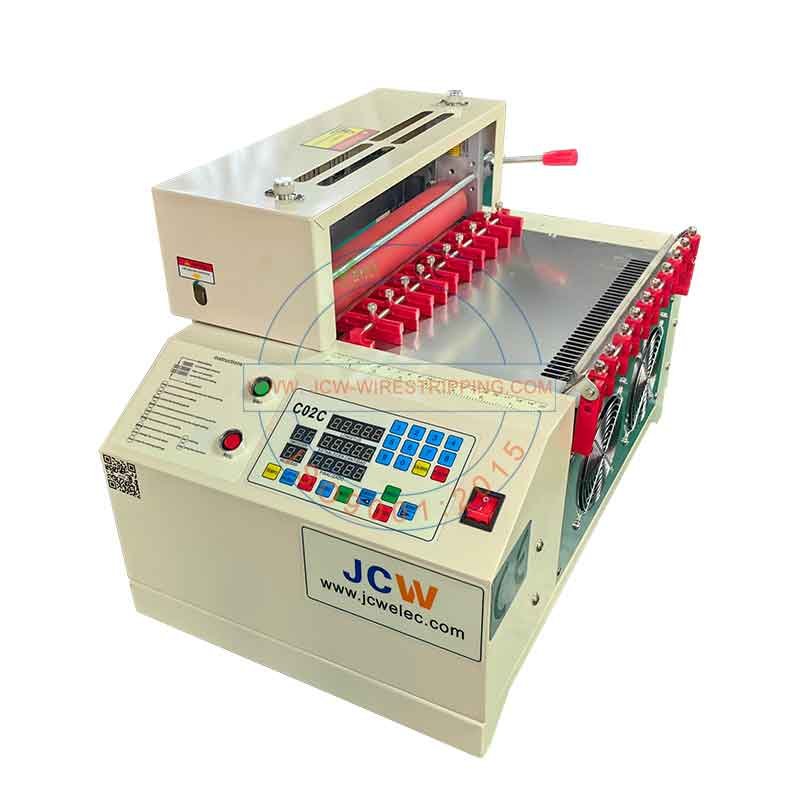
1. Wire harnesses require manual placement, making them less efficient than conveyor belt methods. If efficiency is a priority, consider conveyor belt models.
2. It is not suitable for products with diameters larger than 40mm. For products with large diameters, we recommend using the large-diameter 360-degree heating method.
3. It is not suitable for Teflon products with high temperature requirements.
4. It lacks temperature control and is not suitable for products with delicate temperature requirements. A hot air heat shrink tubing heater should be used instead.
5. It is not suitable for transparent, translucent, or other light-colored heat shrink tubing with poor light absorption.